Synchronization and Ordering Constraints
In this post, our tour through the c++ memory model goes one step deeper. Until now, the posts were only about the atomicity of the atomic data types, but now we deal with the synchronization and ordering constraints of the operations.
You can not configure the atomicity of an atomic data type, but you can adjust very accurately the synchronisation and ordering constraints of atomic operations. Leverage, which is unique to C++. That’s impossible in the C#”s or Java’s memory model.
The six variants of the C++ memory model
C++ has six variants of the memory model. The default for atomic operations is std::memory_order_seq_cst. But you can explicitly specify one of the other five. But what has C++11 to offer?
enum memory_order{
memory_order_relaxed,
memory_order_consume,
memory_order_acquire,
memory_order_release,
memory_order_acq_rel,
memory_order_seq_cst
}
It helps to answer two questions to get a system into the six memory models.
- For which type of atomic operations should you use the memory model?
- Which synchronization and ordering constraints are defined by the memory model?
The rest of this post is about answering these questions. So what are the types of atomic operations?
Types of atomic operations
The memory model deals with reading and/or writing atomic operations.
 Modernes C++ Mentoring
Modernes C++ Mentoring
Do you want to stay informed: Subscribe.
- read operation: memory_order_acquire and memory_order_consume
- write operation: memory_order_release
- read-modify-write operation: memory_order_acq_rel and memory_order_seq_cst
memory_order_relaxed defines no synchronisation and ordering constraints. So it will not fit in this taxonomy.
The table orders the atomic operations based on their reading and/or writing characteristics.
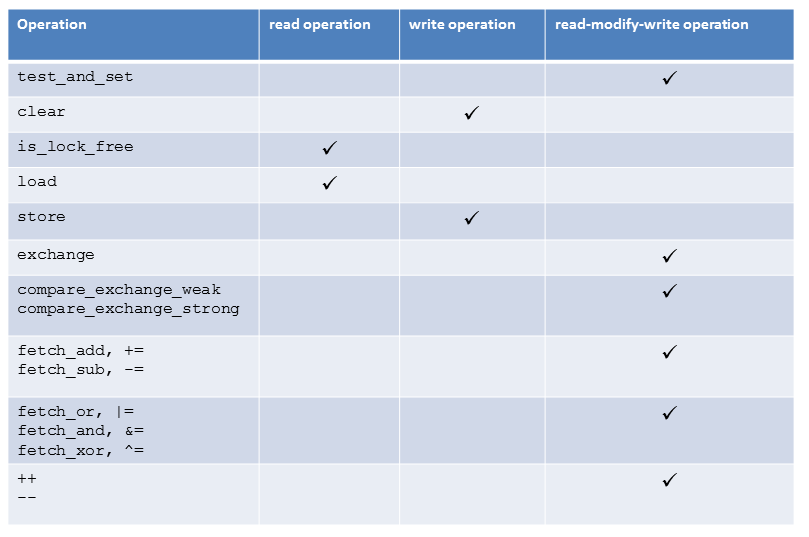
If you use an atomic operation atomVar.load(5) with a memory model designed for a write or read-modify-write operation, the writing part has no effect. So an atomVar.load(5,std, std::memory_order_acq_rel) is equivalent to an atomVar.load(5,std::memory_order_acquire), an atomVar.load(5, std::memory_order_release) is equivalent to an atomVar.load(5, std::memory_order_relaxed).
The different synchronization and ordering constraints
There are three different types of synchronization and ordering constraints in C++11:
- Sequential consistency: memory_order_seq_cst
- Acquire-release: memory_order_consume, memory_order_acquire, memory_order_release and memory_order_acq_rel
- Relaxed: memory_order_relaxed
While the sequential consistency establishes a global order between threads, the acquire-release semantic establishes an ordering between reading and write operations on the same atomic variable on different threads. The relaxed semantic only guarantees that operations on the same atomic data type in the same thread can not be reordered. That guarantee is called modification order consistency. But other threads can see this operation in a different order.
What’s next?
Admit, that was a short post. But I will stick to my idea of discussing only one topic in one post.
Especially the levels of the different memory models and their effects on atomic and non-atomic operations make the C++ memory model a thrilling but also challenging topic. In the next post, I will discuss sequential consistency’s synchronization and ordering constraints, the acquire-release semantic, and the relaxed semantic. I will do it in theory and practice. The following post with be about the application of sequential consistency. The base is laid out in the post sequential consistency.
Thanks a lot to my Patreon Supporters: Matt Braun, Roman Postanciuc, Tobias Zindl, G Prvulovic, Reinhold Dröge, Abernitzke, Frank Grimm, Sakib, Broeserl, António Pina, Sergey Agafyin, Андрей Бурмистров, Jake, GS, Lawton Shoemake, Jozo Leko, John Breland, Venkat Nandam, Jose Francisco, Douglas Tinkham, Kuchlong Kuchlong, Robert Blanch, Truels Wissneth, Mario Luoni, Friedrich Huber, lennonli, Pramod Tikare Muralidhara, Peter Ware, Daniel Hufschläger, Alessandro Pezzato, Bob Perry, Satish Vangipuram, Andi Ireland, Richard Ohnemus, Michael Dunsky, Leo Goodstadt, John Wiederhirn, Yacob Cohen-Arazi, Florian Tischler, Robin Furness, Michael Young, Holger Detering, Bernd Mühlhaus, Stephen Kelley, Kyle Dean, Tusar Palauri, Juan Dent, George Liao, Daniel Ceperley, Jon T Hess, Stephen Totten, Wolfgang Fütterer, Matthias Grün, Phillip Diekmann, Ben Atakora, Ann Shatoff, Rob North, Bhavith C Achar, Marco Parri Empoli, Philipp Lenk, Charles-Jianye Chen, Keith Jeffery, Matt Godbolt, Honey Sukesan, bruce_lee_wayne, Silviu Ardelean, and Seeker.
Thanks, in particular, to Jon Hess, Lakshman, Christian Wittenhorst, Sherhy Pyton, Dendi Suhubdy, Sudhakar Belagurusamy, Richard Sargeant, Rusty Fleming, John Nebel, Mipko, Alicja Kaminska, Slavko Radman, and David Poole.
| My special thanks to Embarcadero |  |
| My special thanks to PVS-Studio |  |
| My special thanks to Tipi.build |  |
| My special thanks to Take Up Code |  |
| My special thanks to SHAVEDYAKS |  |
Modernes C++ GmbH
Modernes C++ Mentoring (English)
Rainer Grimm
Yalovastraße 20
72108 Rottenburg
Mail: schulung@ModernesCpp.de
Mentoring: www.ModernesCpp.org



Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!