Template Arguments
It is pretty interesting how the compiler deduces the types for the template arguments. To make it short, you get most of the time the type you expect. The rules do not only apply to function templates (C++98) but also to auto (C++11), to class templates (C++17), and concepts (C++20).
C++ has supported function template argument deduction since its beginning. Here is a short recap.
Function Template Argument Deduction
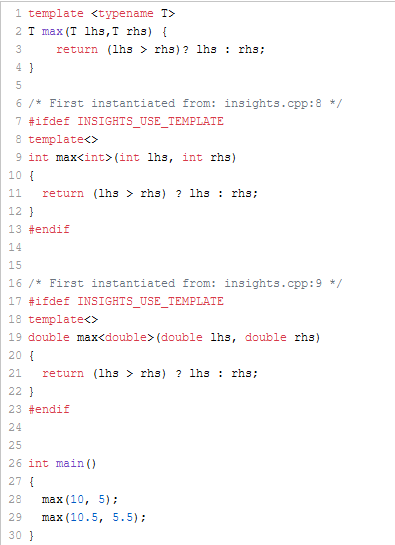
Let me invoke a function template max for int and double
template <typename T> T max(T lhs, T rhs) { return (lhs > rhs)? lhs : rhs; } int main() { max(10, 5); // (1) max(10.5, 5.5); // (2) }
In this case, the compiler deduces the template arguments from the function arguments. C++ Insights shows that the compiler creates a fully specialized function template for max for int (1) and for double (2).
 Modernes C++ Mentoring
Modernes C++ Mentoring
Do you want to stay informed: Subscribe.
The process of template type deduction, such as in this case, produces most of the time the expected type. It is pretty enlightening to analyze this process deeper.
Template Type Deduction
When deducing the template type, three entities come into play: T, ParameterType, and expression.
template <typename T> void func(ParameterType param); func(expression);
Two types are deduced:
TParameterType
The ParameterType can be a
- Value
- Reference (&) or Pointer (*)
- Universal Reference (&&)
The expression can be an lvalue or an rvalue having. Additionally, the lvalue or rvalue can be a reference, or const/volatile qualified.
The easiest way to understand the template type deduction process is to vary the ParameterType.
ParameterType is a Value
Taking the parameter by value is probably the most used variant.
template <typename T> void func(T param); func(expr);
- When
expris a reference, the reference is ignored=> newExpris created - When
newExprisconstorvolatile,constorvolatileis ignored.
If the parameter type is a reference or a universal reference, the constness (or volatileness) of expr is respected.
ParameterType is a Reference (&) or Pointer (*)
For simplicity, I use a reference. The analogous argumentation holds for a pointer. Essentially, you get precisely the result you expect.
template <typename T> void func(T& param); // void func(T* param); func(expr);
- When
expris a reference, the reference is ignored (but added at the end). - The expr matches the
ParameterTypeand the resulting type becomes a reference. This means,- an
exprof typeintbecomes anint& - an
exprof typeconst intbecomes aconst int& - an
exprof typeconst int&becomes aconst int&
- an
ParameterType is a Universal Reference (&&)
template <typename T> void func(T&& param); func(expr);
- When
expris an lvalue, the resulting type becomes an lvalue reference. - When
expris an rvalue, the resulting type becomes an rvalue reference.
Admittedly, this explanation was pretty technical. Here is an example.
// templateTypeDeduction.cpp template <typename T> void funcValue(T param) { } template <typename T> void funcReference(T& param) { } template <typename T> void funcUniversalReference(T&& param) { } class RVal{}; int main() { const int lVal{}; const int& ref = lVal; funcValue(lVal); // (1) funcValue(ref); funcReference(lVal); // (2) funcUniversalReference(lVal); // (3) funcUniversalReference(RVal()); }
I define and use a function template taking its argument by value (1), by reference (2), and by universal reference (3).
Thanks to C++ Insights, I can visualize the type deduction of the compiler.
- (1): Both calls of
funcValuecause the same instantiation of the function template. The deduced type is anint.

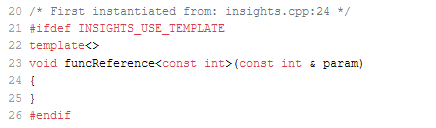
- (2): Calling the function
funcReferencewithconst int&gives the typeconst int&.
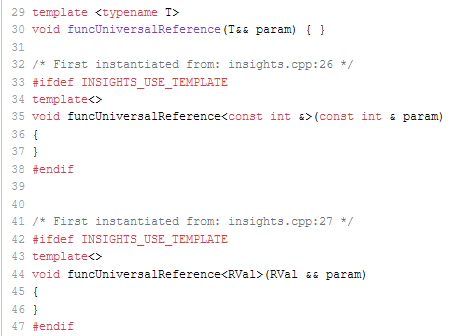
- (3): Using the function
funcUniversalReferencegive an lvalue reference or an rvalue reference.
There is one interesting fact when you invoke the function funcValue with a C-array. The C-array decays.
Decay of a C-array
Taking a C-array by value is remarkable.
// typeDeductionArray.cpp template <typename T> void funcValue(T param) { } int main() { int intArray[10]{ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}; funcValue(intArray); }
When you invoke the function template funcValue with a C-array, the C-array decays to a pointer onto its first element. Decay has many facets. It is applied when a function argument is passed by value. Decay means that an implicit conversion function-to-pointer, array-to-pointer, or lvalue-to-rvalue is applied. Additionally, the reference of a type T and its const-volatile qualifiers are removed.
Here is the screenshot of the program from C++ Insights.

This essentially means that you don’t know the size of the C-array.
But there is a trick. Taking the C-array by reference and pattern matching on the type and the size on the C-array gives you the size of the C-array:
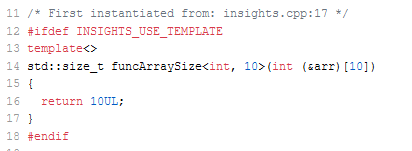
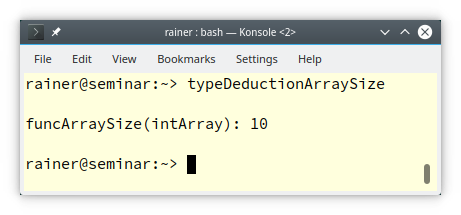
// typeDeductionArraySize.cpp #include <cstddef> #include <iostream> template <typename T, std::size_t N> std::size_t funcArraySize(T (&arr)[N]) { return N; } int main() { std::cout << '\n'; int intArray[10]{ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}; funcArraySize(intArray); std::cout << "funcArraySize(intArray): " << funcArraySize(intArray) << '\n'; std::cout << '\n'; }
The function template funcArraySize deduces the size of the C-arrays. I gave, for readability reasons, the C-array parameter the name arr: std::size_t funcArraySize(T (&arr)[N]). This is not necessary, and you can write std::size_t funcArraySize(T (&)[N]). Here are the internals from C++ Insights.
Finally, the output of the program:
When you understand template type deduction, you essentially understand auto type deduction in C++11.
auto Type Deduction
auto type deduction uses the rules of template type deduction.
To remind you, these are the essential entities of template type deduction:
template <typename T> void func(ParameterType param); auto val = 2011;
Understanding auto means that you have to regard auto as the replacements for T and the type specifiers of auto as the replacements for the ParameterType in the function template.
The type specifier can be a value (1), a reference (2), or a universal reference (3).
auto val = arg; // (1) auto& val = arg; // (2) auto&& val = arg; // (3)
Let’s try it out and change the previous program templateTypeDeduction.cpp and use auto instead of function templates.
// autoTypeDeduction.cpp class RVal{}; int main() { const int lVal{}; const int& ref = lVal; auto val1 = lVal; // (1) auto val2 = ref; auto& val3 = lVal; // (2) auto&& val4 = lVal; // (3) auto&& val5 = RVal(); }
When you study the resulting types in C++ Insights, you see that they are identical to the types deduced in the program templateTypeDeduction.cpp.

Of course, auto decays when it takes a C-array by value.
The New pdf-Bundle is Ready: C++20 Coroutines
What’s next?
C++17 makes type deduction more powerful. First, automatic type deduction is possible for non-type template parameters, and second, class templates can also deduce their arguments. In particular, class template argument deduction makes the life of a programmer much more straightforward.
Thanks a lot to my Patreon Supporters: Matt Braun, Roman Postanciuc, Tobias Zindl, G Prvulovic, Reinhold Dröge, Abernitzke, Frank Grimm, Sakib, Broeserl, António Pina, Sergey Agafyin, Андрей Бурмистров, Jake, GS, Lawton Shoemake, Jozo Leko, John Breland, Venkat Nandam, Jose Francisco, Douglas Tinkham, Kuchlong Kuchlong, Robert Blanch, Truels Wissneth, Mario Luoni, Friedrich Huber, lennonli, Pramod Tikare Muralidhara, Peter Ware, Daniel Hufschläger, Alessandro Pezzato, Bob Perry, Satish Vangipuram, Andi Ireland, Richard Ohnemus, Michael Dunsky, Leo Goodstadt, John Wiederhirn, Yacob Cohen-Arazi, Florian Tischler, Robin Furness, Michael Young, Holger Detering, Bernd Mühlhaus, Stephen Kelley, Kyle Dean, Tusar Palauri, Juan Dent, George Liao, Daniel Ceperley, Jon T Hess, Stephen Totten, Wolfgang Fütterer, Matthias Grün, Phillip Diekmann, Ben Atakora, Ann Shatoff, Rob North, Bhavith C Achar, Marco Parri Empoli, Philipp Lenk, Charles-Jianye Chen, Keith Jeffery, Matt Godbolt, Honey Sukesan, bruce_lee_wayne, Silviu Ardelean, and Seeker.
Thanks, in particular, to Jon Hess, Lakshman, Christian Wittenhorst, Sherhy Pyton, Dendi Suhubdy, Sudhakar Belagurusamy, Richard Sargeant, Rusty Fleming, John Nebel, Mipko, Alicja Kaminska, Slavko Radman, and David Poole.
| My special thanks to Embarcadero |  |
| My special thanks to PVS-Studio |  |
| My special thanks to Tipi.build |  |
| My special thanks to Take Up Code |  |
| My special thanks to SHAVEDYAKS |  |
Modernes C++ GmbH
Modernes C++ Mentoring (English)
Rainer Grimm
Yalovastraße 20
72108 Rottenburg
Mail: schulung@ModernesCpp.de
Mentoring: www.ModernesCpp.org


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!